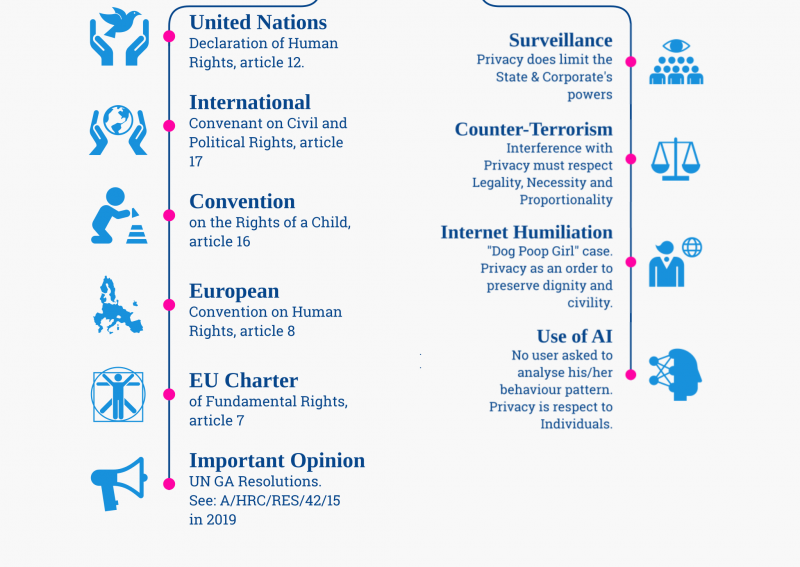
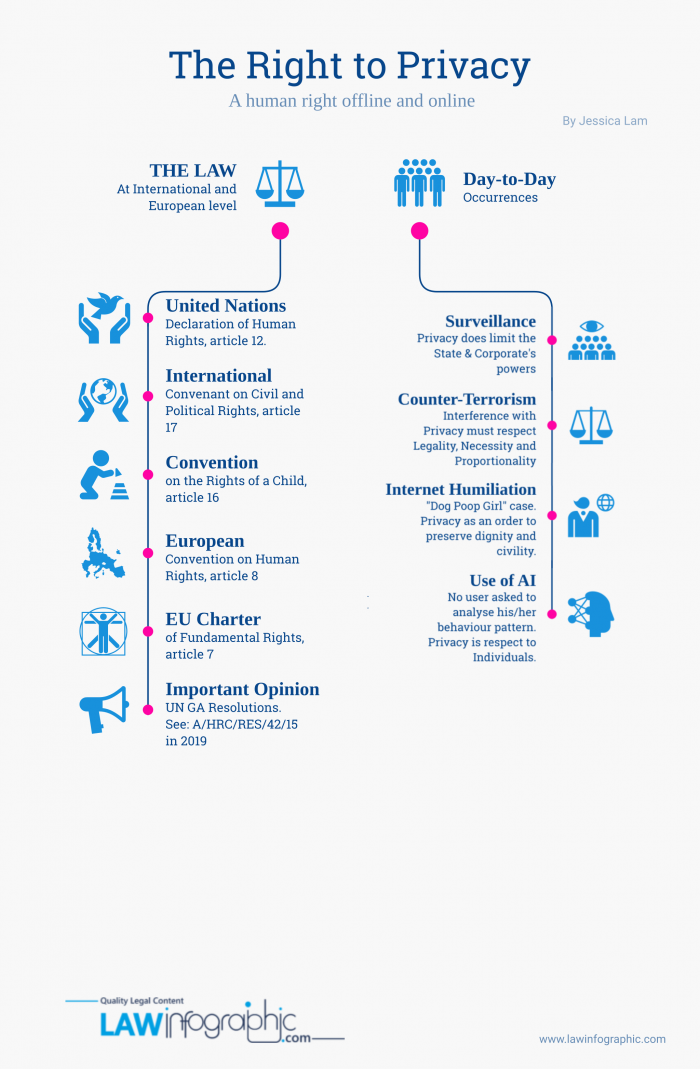
AT INTERNATIONAL LEVEL:
- The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, article 12, defines the Right to Privacy as:
“No one shall be subjected to arbitrary interference with his Privacy, family, home or correspondence, nor to attacks upon his honour and reputation. Everyone has the right to the protection of the law against such interference or attacks.”
Useful? Embed this infographic on your website.
- The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, article 17:
“1. No one shall be subjected to arbitrary or unlawful interference with his Privacy, family, home or correspondence, nor to unlawful attacks on his honour and reputation.
2. Everyone has the right to the protection of the law against such interference or attacks.”
- Convention on the Rights of a Child, article 16:
“1. No child shall be subjected to arbitrary or unlawful interference with his or her privacy, family, home or correspondence, nor to unlawful attacks on his or her honour and reputation.
2. The child has the right to the protection of the law against such interference or attacks.” - UN General Assembly Resolutions: No legally binding instrument, but highly weight opinion on the international community. The last GA Resolution on the Right to Privacy in the digital age was provided in 2019:
“affirms that the same rights that people have offline must also be protected online, including the right to privacy.”
AT EUROPEAN LEVEL:
- The European Convention on Human Rights, article 8:
“1. Everyone has the right to respect for his private and family life, his home and his correspondence.
2. There shall be no interference by a public authority with the exercise of this right except such as is in accordance with the law and is necessary in a democratic society in the interests of national security, public safety or the economic well-being of the country, for the prevention of disorder or crime, for the protection of health or morals, or for the protection of the rights and freedoms of others.”
- The EU Charter of Fundamental Rights, article 7:
“Respect for private and family life Everyone has the right to respect for his or her private and family life, home and communications.”
To me, Privacy is the right to have my personal space respected and my duty to respect the private sphere of others, so we can all live together, in a more or less civilized environment. Otherwise, social friction would jeopardize society and, consequently, all of us.
Privacy also allows us to form our own opinions, participate and engage in activities, and hence, build our personality and identity, enabling the use of other rights, such as freedom of expression or freedom to peacefully assembly and association, the base of any democratic society.
It is not an absolute right, but any interference needs to be consistent with the principle of legality, necessity and proportionality
What I have been reading?
- The UN Digital Library:
https://digitallibrary.un.org/
- “Dog Poop Girl” case: https://archives.cjr.org/behind_the_news/the_tale_of_dog_poop_girl_is_n.php
Jessica Lam
Latest posts by Jessica Lam (see all)
- Processing Personal Data - March 30, 2021
- What is Privacy? - February 25, 2021
- What is Privacy Engineering? - January 14, 2021